Studies have suggested that over 90% of content gets no traffic from Google. Given this fact, it obviously follows that there are plenty of entire websites getting no SEO traffic at all.
If you’ve noticed that your site is getting little-to-no traffic from Google, we’ll walk through:
- How to determine why you’re not getting organic traffic.
- How to address the issues holding your site back.
- How to monitor your traffic and the types of issues preventing you from generating SEO traffic moving forward.
Let’s dive in!
Contents
- Your reporting is messed up
- Your website isn’t getting indexed
- You have no (or few) backlinks
- You’re not targeting the right keywords
- Your site has been penalized
5 reasons you’re not getting website traffic (+what to do about it!)
Here, we’ll walk through each of the top reasons you’re not seeing traffic to your site and what you can do to fix it.
1. You’re having reporting issues
The first question to ask yourself is whether the tool you’re using to report on organic traffic is accurate (and if you’re using it right).
Here’s what to do about it.
Check Google Analytics 4
A lot of people don’t like GA4, and if you’re not used to using that tool, you may be using filters incorrectly.
You can quickly check for the existence of organic traffic from search engines by going to reports > acquisition > user acquisition and looking at the First user primary channel group:
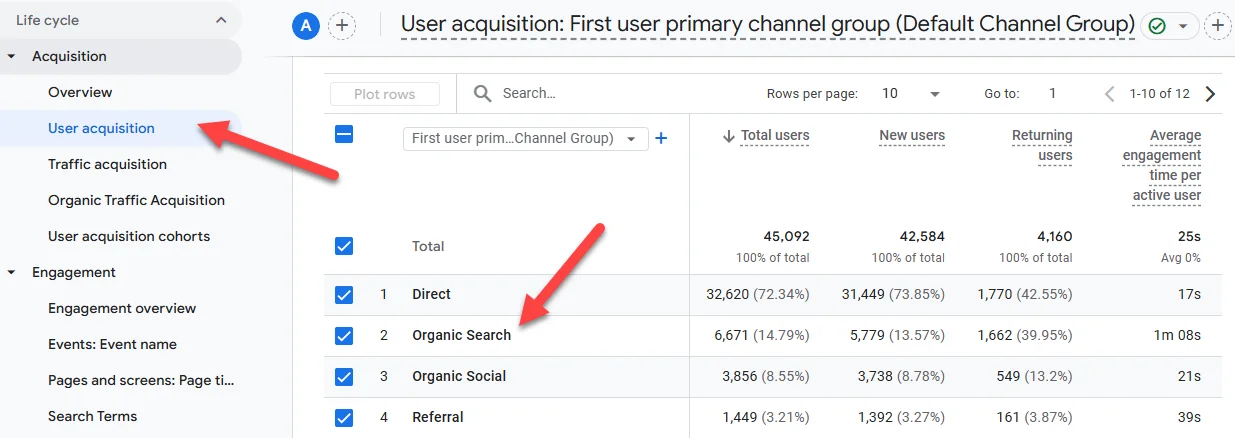
In any view where you’re expecting to see organic search traffic but aren’t, make sure it’s not being filtered out:
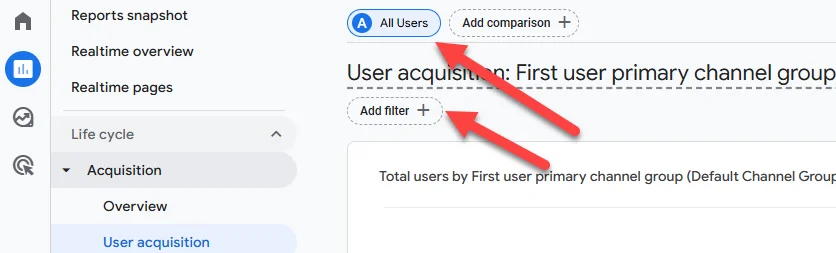
If you’re looking at an exploration in GA4, the same principles would apply: make sure you understand the way the report is set up and are aware of any filters being applied.
👀 Looking for ways to drive people to your site? Free guide >> 25 Ways to Increase Traffic to Your Website
Check Google Search Console
If you’re not seeing traffic in Google Search Console, the filtering issue won’t be traffic source (as it’s showing you only Google-specific traffic), but could be another issue:
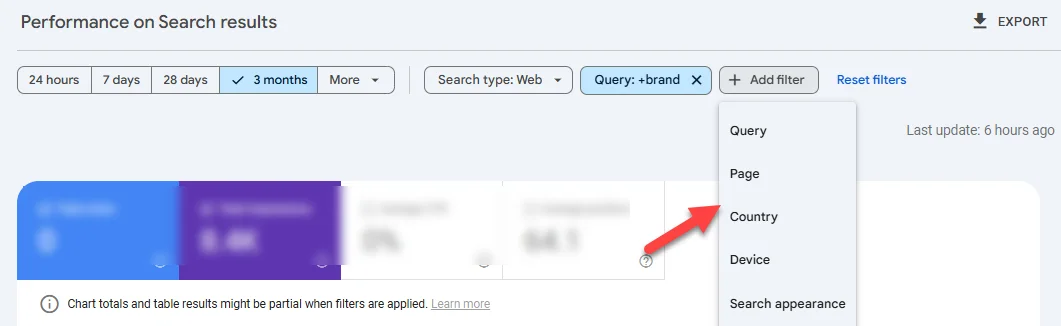
Make sure you’re not filtering by queries, page, etc.
2. Your website isn’t getting indexed
Assuming you’ve checked the tools with which you’re measuring traffic and have confirmed that you are legitimately not getting traffic from SEO, the first thing to confirm is that your pages are actually getting indexed.
Here’s what to do about it.
Confirm your site is (or isn’t) getting indexed
First, check to see if your site is getting indexed. You can do that in two ways:
1. Site search operator: You can quickly see if your site has pages indexed by using a site search operator. Go to Google and type in site:yoursite dot com and see what results are showing. You should see results like this:
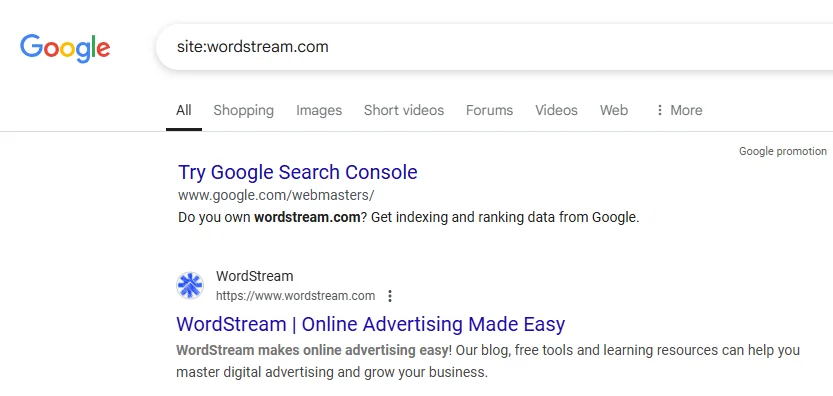
And not results like this:

If you have Google Search Console set up, you can receive even more robust reporting on which pages on your site are indexed and their current status.
2. Google Search Console: Once you see the breakdown of not only the pages on your site that aren’t indexed, but also the reason, you can start to address issues:
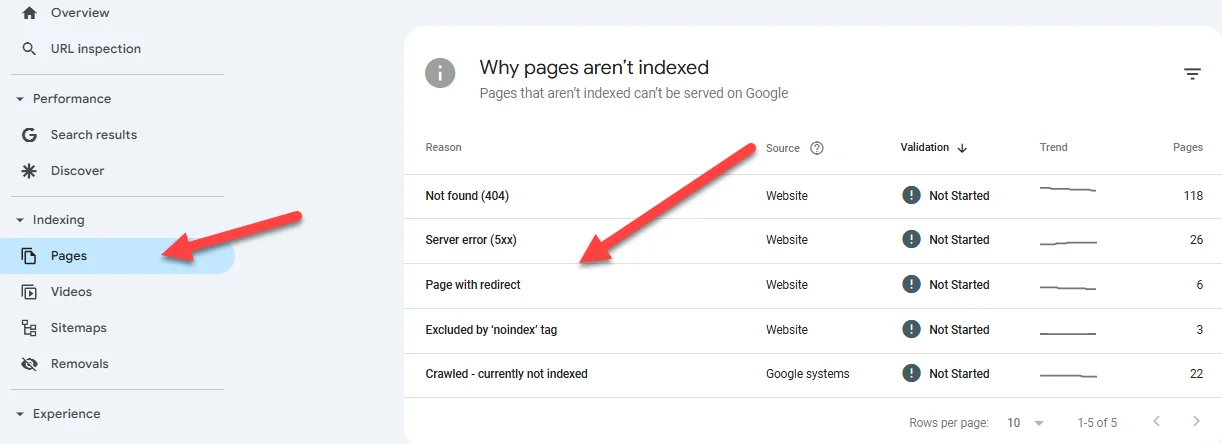
In this screenshot, we see a few different problems:
- Broken links (a page may have been deleted or have another issue) and server errors.
- Pages that have been redirected or excluded by a noindex tag (more on this shortly).
- Pages have been crawled, but are not indexed.
Pages that have been crawled and not indexed or “discovered but not crawled” are often the result of Google not deeming your site sufficiently authoritative and/or not deeming those pages valuable and unique (more on addressing these issues later as well).
Check for technical issues
If you’ve found that your site isn’t getting indexed, there are a few particularly common issues that could lead to pages on a site not being indexed.
- Meta noindex tags: Often times when a developer is building a staging version of your site they’ll add meta noindex tags to the entire site, to keep Google from crawling and indexing the site before it’s pushed live. It’s also not uncommon for the dev team to fail to remove those tags. If you see a large volume or spike of pages not indexed for this reason in Search Console, this is something to investigate.
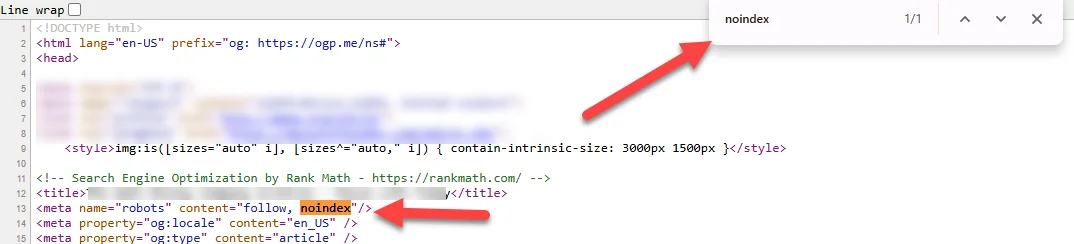
You can look at the source code of a page and search for the noindex tag.
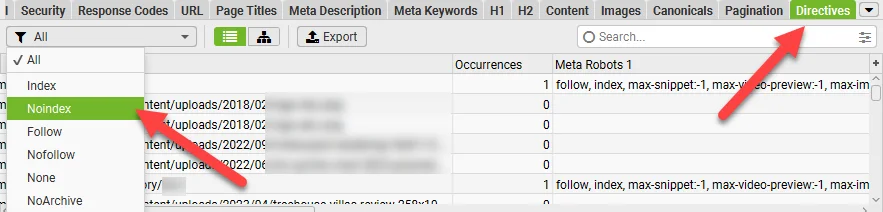
You can also use a tool like Screaming Frog to crawl your site and identify pages that are noindexed.
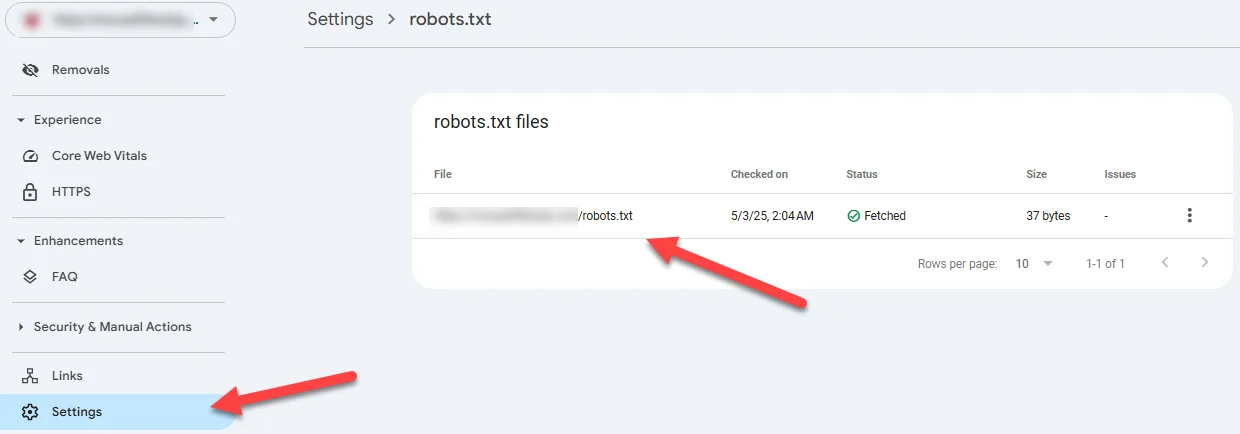
- Robots directives: Your site’s robots.txt file could also be blocking search engines from crawling (and ultimately indexing) your site. You can check the file itself (yoursite dot com/robots.txt) or look for more information in Google Search Console:
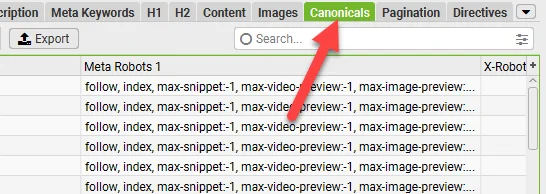
- Canonical tags: A third issue you could be encountering is that a site’s canonical tags may be pointing to a different site entirely. Again, you can check these by looking at the source code on a page, or crawling the site with a tool like Screaming Frog:
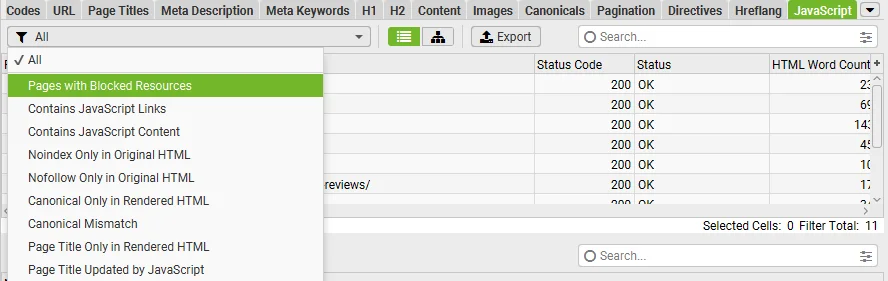
- Lack of crawlable content: If your content is hidden behind a login, JavaScript, or an element Google isn’t able to interact with, you may not be giving that content a chance to rank in search results. Again, Screaming Frog or other technical SEO tools can help diagnose these issues:
🚀 Free guide >> Tangible & Free Ways to Get on the First Page of Google
3. You have no (or few) backlinks
If you’ve confirmed that you’re reporting traffic correctly and that there aren’t specific technical issues preventing your site from being indexed and showing in search results, another issue may be a lack of links to your site.
If you’re hoping to get any kind of significant search traffic to your site, you’re going to need to build links over time. As your site first launches, you may not be showing in any search results because your site has zero or very few links. This can be particularly likely if your brand name is something generic that existing companies already have as a name (e.g., Apex), as you may not rank for even your own brand name.
A quick way to address this is to build local citations for your business, and then start to work on different link-building tactics if you’re hoping to grow your site’s organic traffic.
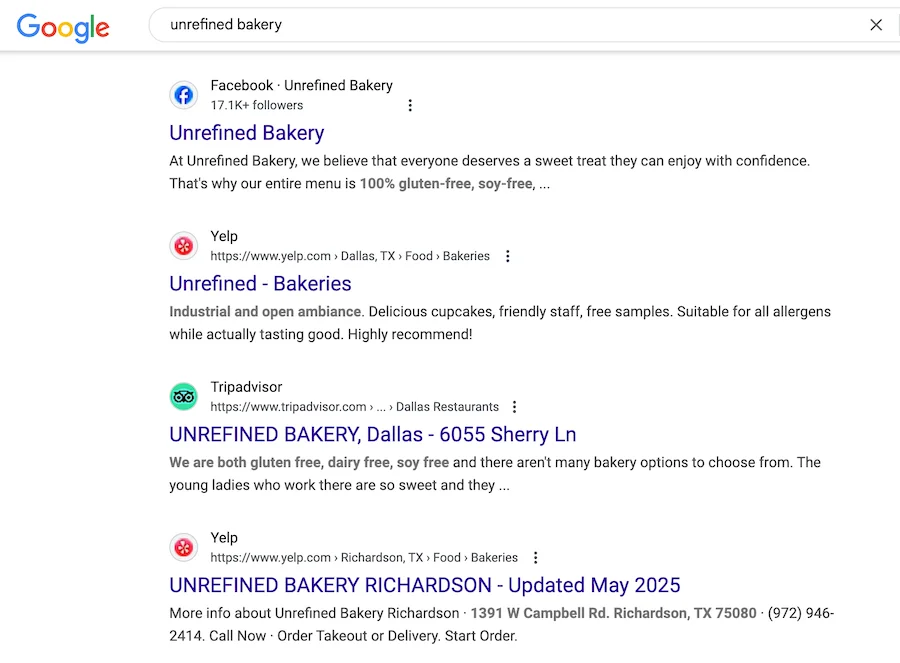
Some examples of local citations for this bakery that can act as backlinks.
4. You’re not targeting the right keywords
If your site already has a baseline of some links, and you’re still not seeing any traffic from SEO, keyword targeting could be the issue.
Again, if you don’t have a unique brand name, your pages may be:
- Targeting search terms that don’t have sufficient search volume.
- Targeting search terms that are too competitive for the site to rank for.
If you’re using GA4 and not seeing any organic traffic, you can use Google Search Console to see not just clicks but also impressions:
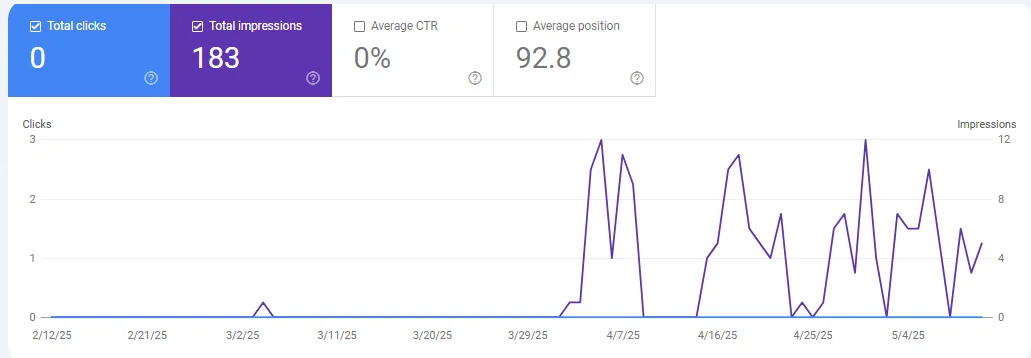
And of course, you can use third-party keyword research tools to identify keywords that have search volume as well.
As you identify relevant keywords, you want to build content that provides value while looking for internal and external linking opportunities to those pages to help drive organic traffic to them.
5. Your site has been penalized
If you do have links pointed to your site as well as relevant content that targets low competition keywords with search volume, there’s a chance your site has been penalized and will be unable to rank.
Here’s what to do about it.
Check for manual penalties
The most clearly identifiable penalty is a manual penalty, which is the result of a manual review of your site where a Google Quality Rater flagged your site as spam. You can identify these in Google Search Console:
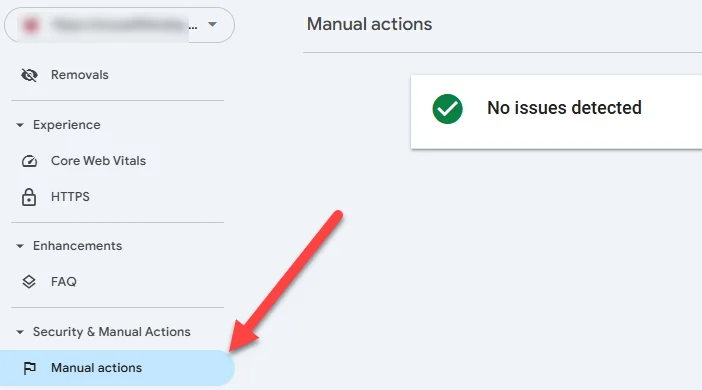
If you do have a manual action, there will typically be some information about the nature of the penalty, example URLs of the offense, and you’ll have an opportunity to submit a request for re-inclusion.
Manual penalties can often be difficult to remove and require significant time and effort, but there is at least a feedback system and some indication directly from Google as to why your site has been penalized.
Look into recent algorithm updates
If your site is adversely impacted by an algorithm update, on the other hand, you won’t be given any information by Google and will have to try to self-diagnose the issue with your site.
If your site had been receiving traffic and then it dropped off, you can start by trying to correlate the drop with Google’s algorithm updates, which they list here.
The most common causes of traffic drops to zero when it comes to being penalized are:
- Low-quality links, particularly at scale.
- Low-quality content, again, particularly if you were generating it and having it indexed at scale.
If you were using a vendor or someone inside your organization was doing SEO for you and you weren’t exactly sure what tactics they were using, investigating the links they were building and the content they were creating on your behalf is a good place to start.
Look at your domain history
If you investigate the activities you’ve taken on your site and there’s no manual action, you may have a historical issue with your domain. If you purchased this domain and there are existing links pointed at it, those may be causing you an issue. Third-party tools like Semrush and Ahrefs allow you to see the links pointed to your domain–looking at these to determine if this may be the cause of an issue is again a good place to start.
Monitoring and addressing SEO issues moving forward
Getting zero SEO traffic can be frustrating, but as we’ve seen, there are often clear, identifiable reasons for this problem. The key is to work through a systematic diagnosis process:
- Verify your reporting tools are correctly set up and not filtering out organic traffic.
- Confirm your pages are being indexed by Google.
- Address any technical barriers like noindex tags, robots directives, or canonical issues.
- Build a foundation of quality links if your site lacks authority.
- Ensure you’re targeting realistic keywords with actual search volume.
- Investigate potential penalties or domain history problems.
It’s also important to keep in mind that even after fixing these foundational issues, it may take time for Google to recrawl your site and for rankings to improve.
Set up regular monitoring through Search Console and GA4 to catch any new issues early and consider implementing technical SEO audits to ensure your site remains healthy from an SEO perspective.
And if you’re stuck troubleshooting a particularly challenging SEO issue, you may want to consider consulting with a professional who can do additional troubleshooting and provide more targeted guidance based on your specific situation.