AI search has a clarity problem. It can access almost everything published online, but it still struggles to understand what each page represents.
When Google’s AI Overviews or ChatGPT pull information, they need more than text. They need to understand who created the content, what the page is trying to achieve, and how it fits within the broader context of your site.
Schema markup provides that structure. It turns unstructured content into clearly defined elements that machines can interpret with confidence.
Contents
- What is schema markup?
- Why schema is important in 2026
- The core schema types driving AI discoverability
- Advanced schema types to try for 2026
- How to implement schema for AI search readiness
- How to measure schema impact
What is schema markup?
Schema markup, also known as structured data, is a type of code that you add to the backend of your website to help search engines get a better understanding of your content.
We cover schema in more detail here.
⬇️ Download our Small Business Website Trends Report to find out how businesses are planning and thinking about AI search and their web presence.
Why schema matters now
Research from Similarweb and Search Engine Land shows that pages with structured data appear more often inside AI Overviews and other rich result formats. As AI-driven search becomes the primary way people interact with results, that pattern becomes a clear competitive advantage. Schema is no longer a technical add-on. It is a core signal that helps AI decide which sources are most reliable.
Schema works because it explains the purpose of each page. It shows that a HowTo page contains steps, a product page includes pricing and ratings, and an article has a real author behind it. With that structure in place, AI tools no longer have to guess what your content means. They can reuse it accurately and with more confidence.
The impact is easy to see in the real world.
Here’s an example from The Zebra, a small insurance comparison startup that competes with much larger brands. Their educational pages use structured FAQ, rating, and Article schema to break down complex topics like insurance costs, deductible types, and state-by-state rules. You can see their markup in use on pages such as the one below.
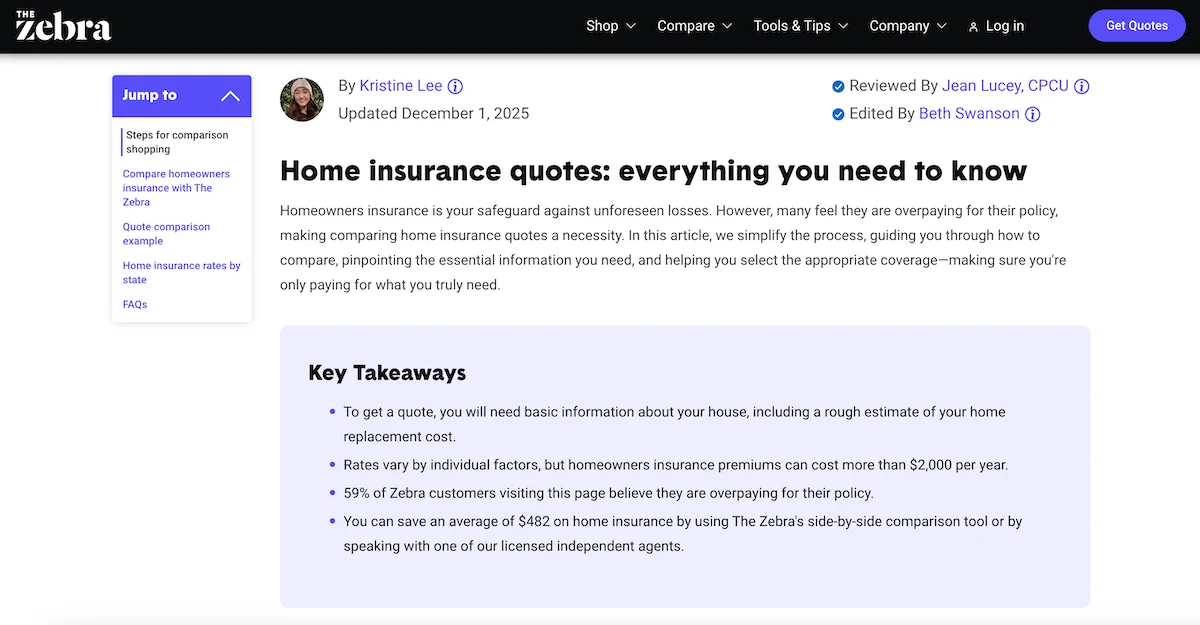
Schema matters because AI engines prioritize sources they can interpret and verify. When your pages communicate their purpose cleanly, your content becomes easier for AI to surface, reuse, and recommend.
The core schema types driving AI discoverability
Let’s take a deeper look at the types of schema you can use to get found by AI search engines.
1. FAQ schema: Turning expertise into reusable knowledge
FAQ schema works well because it mirrors how people interact with AI tools. Users ask conversational questions, and AI returns concise answers. When your page already contains structured question-and-answer pairs, AI systems can extract and reuse them with higher confidence.
FAQ schema is most effective when you answer real questions that customers actually ask. The best sources are support tickets, onboarding friction, and common objections. These questions reveal genuine user intent, and AI systems prioritise information that addresses real problems.
A clear example comes from Warby Parker, which uses well-structured FAQ markup across its help center. Their Q&A covers shipping, prescriptions, insurance, and returns, and you can see their markup in action here:
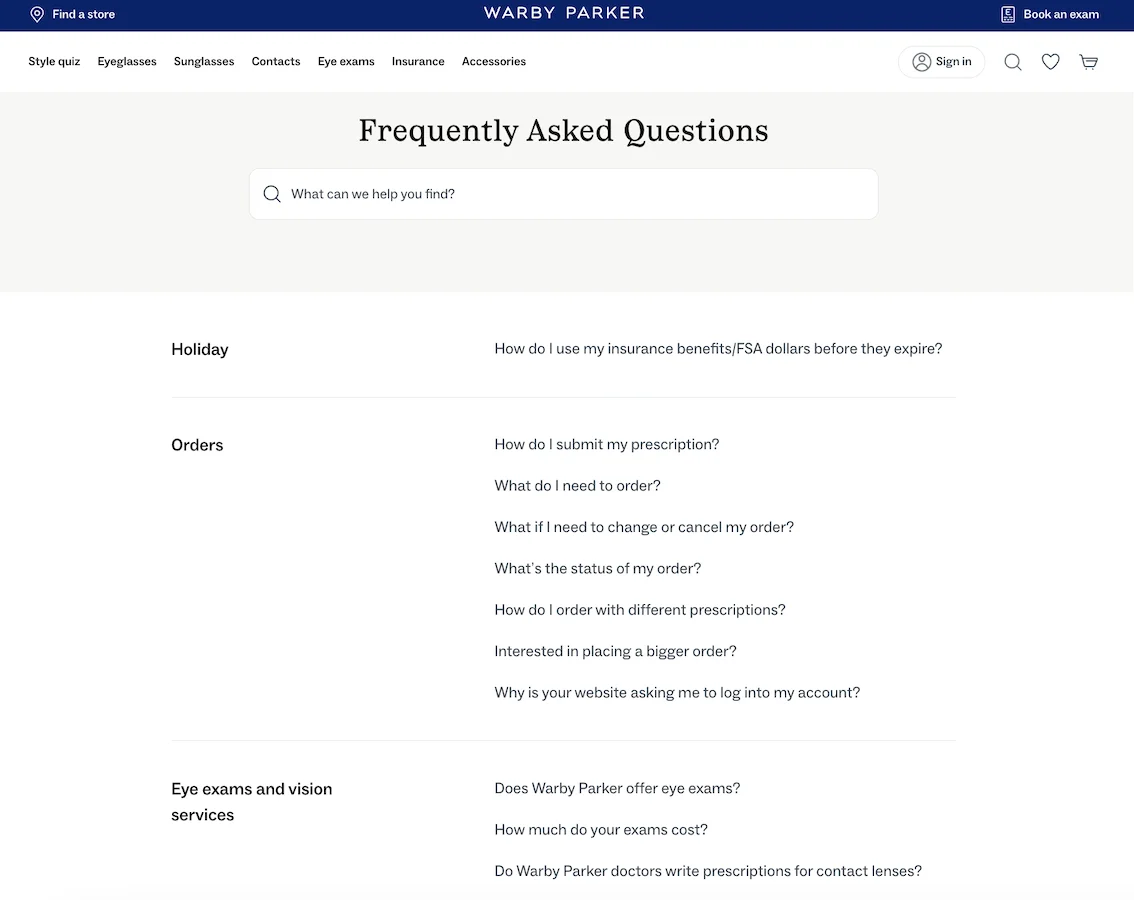
These structured FAQs surface frequently in rich results for searches like “How do I set up a return or exchange?” or “Does Warby Parker offer eye exams?” The content is simple, direct, and structured in a way that makes it easy for search engines and AI systems to understand and reuse.
FAQ schema works because it teaches. It turns your answers into reusable knowledge that AI tools can reference confidently across conversational queries and overview-style summaries.
🔎 Need help understanding the modern rules for SEO? Download our free guide >> How to Do SEO Right—Right Now!
2. HowTo schema: Helping AI surface step-by-step instructions
HowTo schema turns tutorials into structured sequences that AI tools can interpret instantly. If you write how-to content, you should treat it as instructional documentation rather than long-form commentary.
AI engines prefer clear, numbered steps with simple phrasing. They look for stages, prerequisites, and actions. The goal is not to impress with lengthy explanations but to guide the reader through a process in a predictable structure.
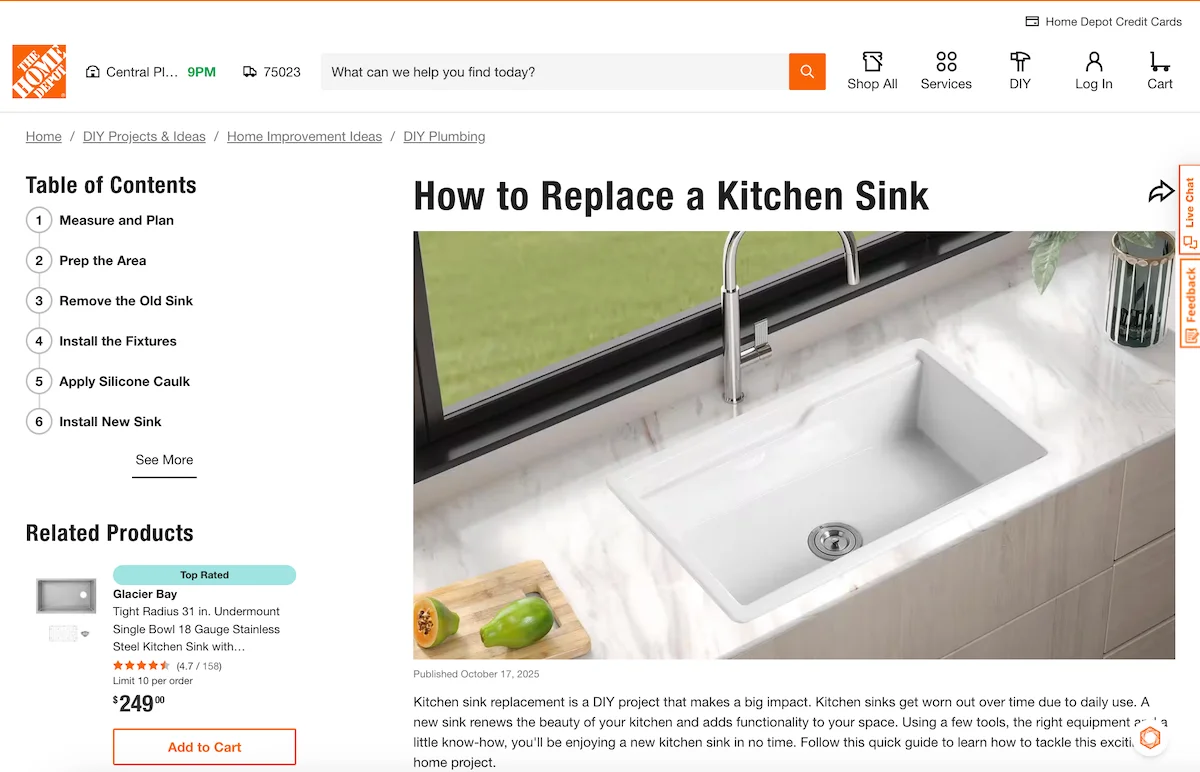
Here’s an example of an article using HowTo schema.
For example, if you explain “How to optimize product images for SEO,” avoid embedding steps inside long paragraphs. Break them into clean units: compress, label, resize, add alt text, and upload. When each step is clearly defined and supported by HowTo schema, AI engines can confidently reuse those instructions in an overview.
Creators who use HowTo schema consistently often see their tutorials reused not only in search results but also in voice outputs and chat-style answers. That happens because AI tools can see the logic of the content, not just the text.
If your brand produces educational content, HowTo schema is one of the most valuable tools you can add.
3. Author and person schema: Helping AI verify real expertise
AI engines need to know who is behind the content they surface. When a page has no identifiable author or verifiable background, AI systems treat it as lower-trust information. Clear authorship helps AI understand that a real expert created the content.
Author schema provides that signal. It supplies a name, role, credentials, and affiliation in a format AI can cross-reference with your broader digital presence.

This blog post includes the author and medical reviewers to further the credibility of the content.
When those details align with your organization’s schema and external profiles, AI can confirm that the author is legitimate and consistent across platforms.
This philosophy matches how reputable publishers operate. As Stephanie Heitman, Associate Director of Content at WordStream and LocaliQ, explains: “Author credibility is extremely important to us. By publishing content written by an industry expert, we feel that we can provide our audience with the most relevant, up-to-date, and insightful information to help them stay tuned into the latest digital marketing news, trends, and tips. That’s why we publish content not only written by our in-house experts but also by outside experts to add even more unique insights to our blog.”
AI systems apply a similar logic. When they condense multiple sources into a single answer, they prioritize content tied to recognizable experts. Strong bios, linked credentials, and a visible publication history help AI determine whose insights to trust.
Author schema reinforces this by linking each article to a specific, verifiable person. Once AI can see that the same expert consistently publishes on a topic, both the individual and the brand gain authority in generative results.
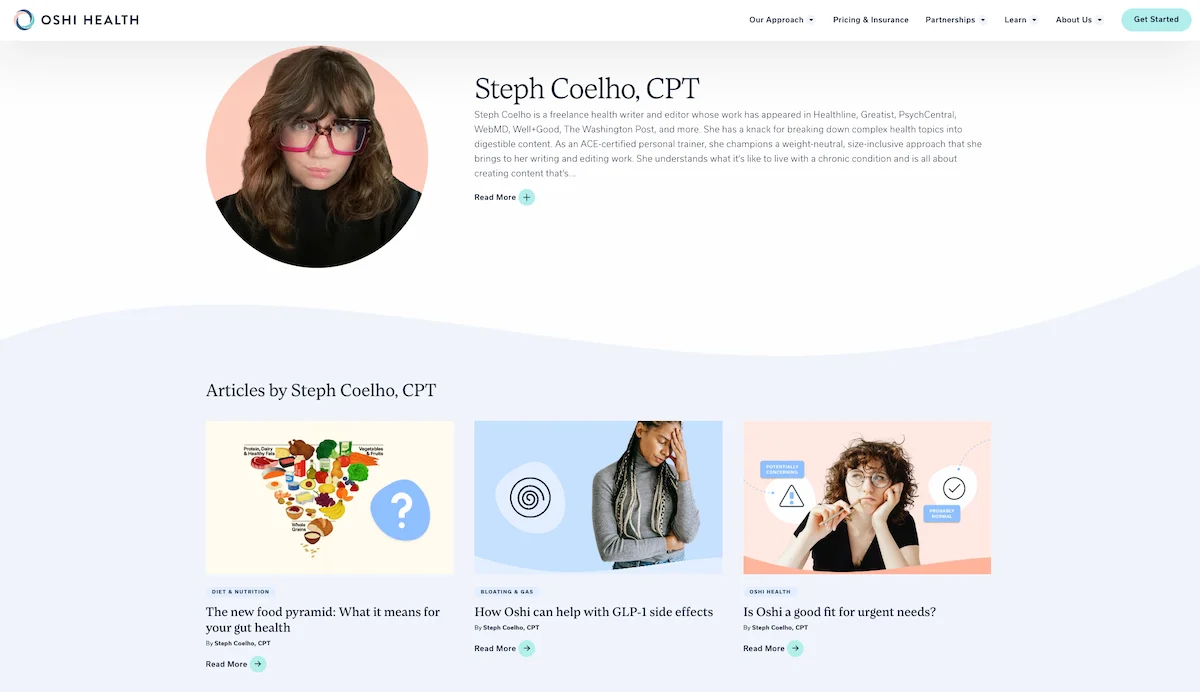
This author’s page includes all her posts on this site and her credentials in her author bio.
For websites that publish educational or advisory content, this schema type is essential. Anonymous articles or generic team credits rarely perform well in AI-driven search because the expertise cannot be confirmed. When your authors are clearly represented and supported by structured data, your content becomes far easier for AI systems to trust, reuse, and cite.
4. Product and Review schema: Teaching AI how your products work
Product and Review schema help define what you sell and how customers experience it. AI engines depend on this structure to understand a product’s attributes, compare it to alternatives, and decide when it is relevant to a user’s query.
Product schema clarifies features, pricing, availability, and variations. Review schema adds social proof by summarizing customer feedback in a consistent, machine-readable format. Together, they give AI a complete picture of what the product is, how people rate it, and why it might fit a specific search intent.
A solid example is Grove, a mid-sized ecommerce brand focused on sustainable home and personal care products. Their product pages include detailed Product, Offer, and Review markup that covers ingredients, price, stock status, and thousands of verified customer reviews. You can see this implementation here:
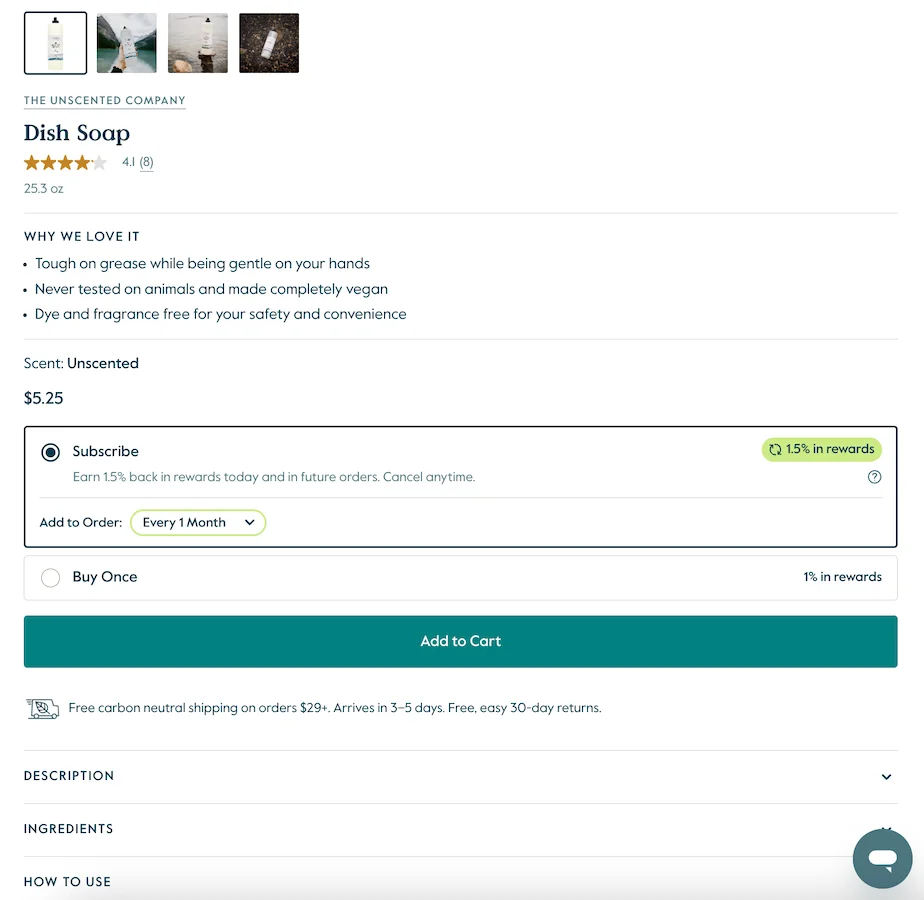
Because their data is structured, Grove often appears in rich shopping results, comparison modules, and AI-generated summaries for queries about eco-friendly cleaners, natural dish soap, and non-toxic household products. The product descriptions were not rewritten. The structured markup made it easier for search and AI systems to understand and surface the information.
The clearer you make your product data, the easier it is for AI tools to match your offerings to relevant queries and present them accurately in generated answers.
5. Organization schema: Helping AI understand your identity
Organization schema ties all your digital signals together. It tells AI that your website, social profiles, videos, and public mentions belong to one unified brand. Without that connection, AI systems treat each signal separately, which weakens your visibility and makes your content harder to verify.
AI engines look for patterns across the web. Inconsistent naming, scattered profiles, or missing links create ambiguity. When your Organization schema defines your logo, founders, social channels, and contact points, AI can confirm that all of those references point to the same entity.
You can see this clearly with Made In Cookware, a mid-sized cookware company that structures its About page with Organization markup linking to its social profiles and brand identifiers.
Because their authors, products, and FAQ pages all reference the same Organization @id, AI systems can recognize the entire site as one connected network. This strengthens the impact of every other schema type they use, from Product to Review to Article markup. Their content becomes easier for AI to interpret and more reliable for AI to surface in results about cookware materials, chef recommendations, and buying guides.
Schema works best when it builds relationships. Organization schema is the foundation that allows AI engines to understand who you are, how your content fits together, and why your brand should be included in generative answers.
🎉 Need help articulating what makes your business special? Get the guide >> How to Create a Unique Value Proposition From the Ground Up
Advanced schema for 2026: Underused but highly effective
Some schema types rarely get implemented, yet they carry outsized influence in how AI engines interpret your content. These formats give AI the contextual signals it needs to understand what your page represents beyond surface-level text.
- VideoObject and Transcript: AI models give more weight to video content when it includes transcripts. VideoObject schema helps AI extract context, and transcripts ensure the model understands the material accurately.
- Speakable: Ideal for voice search and news-style summaries. It highlights the parts of your content that are appropriate for short spoken answers.
- SoftwareApplication: Critical for SaaS companies. It clarifies key properties like pricing, features, and operating systems. AI engines often use this schema to compare software tools.
- Course and Event: Useful for educational brands, coaches, and community organizations. AI tools use these types to surface upcoming events, sessions, and training.
- LocalBusiness and Service: Essential for local visibility. They help AI understand what you do and who you serve in your geographic area.
These schema types work because they describe context that AI systems struggle to infer from plain text alone. They turn your content into structured knowledge.
How to implement schema for AI search readiness
You don’t need to roll out every schema type at once. Start small and focus on the pages that matter most. Once you get the hang of it, you can expand your structure across the rest of your site.
A simple workflow looks like this:
- Pick one high-value page.
- Add the schema type that fits that page best.
- Run it through Google’s Rich Results Test to make sure the markup is valid.
- Compare your schema to the visible page content to avoid contradictions.
- Revisit it every few months to adjust, clean up, or add new fields.

One thing to keep in mind: don’t force multiple entity types into a single block of schema. Use the @id property to connect them instead. AI engines cross-check your markup with the content on the page, so inaccurate or exaggerated fields can weaken trust.
If you’re working with a lot of pages, tools like Rank Math, Yoast, and Schema Pro make it easier to automate the markup and keep everything consistent.
🚀 Free guide >> 10 Tangible & Free Ways to Get on the First Page of Google
How to measure schema implementation impact
Structured data will not always drive more clicks, especially now that so many searches end without one. What it does improve is your visibility. Strong schema increases the chances that AI systems will surface your content in summaries, comparisons, and generated answers.
Here are a few simple ways to track what is happening:
- Check Google Search Console’s Enhancements reports to see if impressions are rising.
- Use tools like Authoritas or OnCrawl to monitor how often you appear in AI Overviews.
- Run industry prompts through ChatGPT or Gemini to see if your content gets referenced.
- Track brand mentions with tools such as Perplexity Labs or BrandMentions.
![]()
Over time, you should notice higher impressions, more AI-based visibility, and a wider range of topics where your content gets reused.
Schema as your AI translator
Schema is the format AI understands best. When your pages are structured clearly, you make it easier for AI engines to interpret your content, your authors, and your products. That clarity leads to better visibility and more frequent citations in generated answers.
The easiest way to start is to structure one page, validate it, and then move on to the next. Each step strengthens the larger network of signals that AI systems use to confirm your expertise.
Brands that treat schema as part of their content strategy, not a technical afterthought, will be the ones AI tools recognize and reference. That recognition will shape visibility in 2026 and beyond.