According to a 2020 study, mobile traffic has grown 504% in daily media consumption since 2011. With more and more consumers using their mobile phones to access content, it’s more important than ever to optimize for the mobile experience—not just for your readers, but for your SEO; Google can detect pages that load slowly or that have a high bounce rate, and will rank those pages lower in search results.
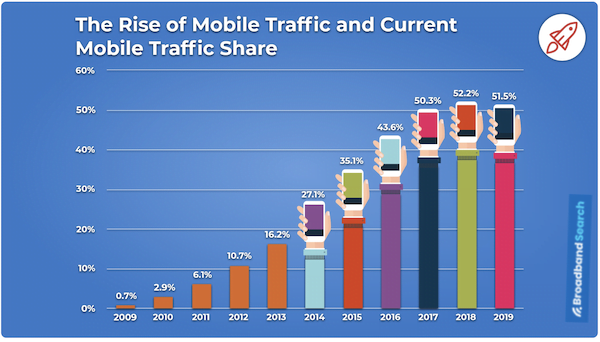
We know that mobile optimization is important for your content strategy and SEO, and Google AMP is a technology designed to help with that, but whether Google AMP is the best tool to do that for your business website, in particular, depends on your industry, business size, business model, content strategy, and more. So in this post, I’m going to cover:
- What Google AMP is, who it’s best for, and how it works.
- The benefits and drawbacks of Google AMP.
- How to implement AMP on your site, if it’s right for you.
Regardless of whether Google AMP ends up being right for you, you’ll come away from this post with the SEO knowledge you need in order to feel confident about your site’s SEO and mobile performance.
What exactly is Google AMP?
In 2016, Google announced the launch of Accelerated Mobile Pages—an open-source, web-based solution designed to revolutionize mobile content consumption. It was a direct response to Facebook’s then in-app publishing platform (Instant Articles), and Apple’s iOS 9 news aggregation and discovery platform (Apple News).
The AMP version of a product page, blog post, or landing page is meant to load instantly on mobile. It may also appear differently or in a card form in the mobile SERP. The AMP lightning bolt symbol associated with a result lets users know that that particular page will load faster than other non-AMP pages around it.

According to an early study, Google AMP pages load four times faster and use eight times less data than traditional mobile-optimized pages. The initial idea was to provide an open-source framework that would make the mobile experience not just better, but faster.
The initial idea was to provide an open-source framework that would make the mobile experience not just better, but faster.
Is AMP essential?
Before we get into the pros and cons of Google AMP, it’s important to note that while AMP can help your SEO, it is not necessarily essential for SEO in some cases, and the benefits are more applicable to some businesses than others. We will do a deeper dive into the pros and cons of AMP next, but let’s first just provide some key points that can help you orient yourself to AMP as it relates to your business:
- AMP is widely adopted by publisher sites that have a high volume of news articles or blog posts. If the majority of your website pages aren’t articles, then AMP may not be necessary for your business.
- If you do publish a high volume of articles but are already using a CDN (content delivery network), these platforms often come with performance optimization features such as image hosting, file caching, and lazy loading (which means the text loads first, before the images).
- AMP pages are cleaner and simpler for readers, but often because certain JavaScript functions and plugins are deprioritized or suppressed. If you rely on third-party tools for lead capturing and audience tracking, you’ll want to test to make sure your AMP pages function and capture information the same as your regular pages.
- AMP itself is not a Google ranking factor. It can help improve aspects of your web pages that are factored into Google’s algorithm (especially with Core Web Vitals becoming a ranking factor in 2021), but it is not the only way to optimize your site’s experience and performance.
- If you already have a mobile version of your site or mobile optimization measures in place (such as consolidated or minified CSS code), AMP may not be necessary and may even complicate performance and reporting.
While AMP can help your SEO, it is not necessarily essential for SEO, and its benefits are more applicable to some businesses than others.
So the bottom line is, optimizing for page speed and mobile experience is essential for SEO, and Google AMP is just one way of achieving that. Read on to learn about how it works and whether it’s the right solution for your business.
What are the benefits of Google AMP?
Apart from faster loading speeds and a better experience for content consumers, AMP offers several benefits to businesses with a content and SEO strategy:
Increased website engagement
Lightweight AMP content meshes well with mobile users that have a less-than-stable internet connection. Additionally, the decrease in page load time improves the user experience in a way that increases the chances of visitors staying on your site longer.
Improved ranking and traffic
Also, with page load time being a Google ranking factor, AMPs are prioritized in Google’s search algorithms, thus affecting rankings. Essentially, if two sites are neck-and-neck, the faster one wins out.
Lower bounce rates
With your pages loading faster, visitors usually stay onsite. A Google study once found that 53% of website visits are abandoned if a mobile site takes longer than 23 seconds to load. Additionally, publishers who implement AMP could potentially get a 2x increase in time spent on a page. And more time on your website can mean more conversions from your content.
More time on your website can mean more conversions from your content.

Increased ad views
With AMP, the HTML is coded in a way that enhances the overall usability of banners and images. This results in a higher ad viewability rate, helping publishers to increase opportunities for monetizing their content.
Higher click-through rates
A major benefit of AMP is that it is showcased in the Top Stories list (or carousel) of the Google mobile SERP—which appears on top of all search results. Readers are highly more likely to select those AMP pages first, leading to increased click-through rates.

Current AMP statistics
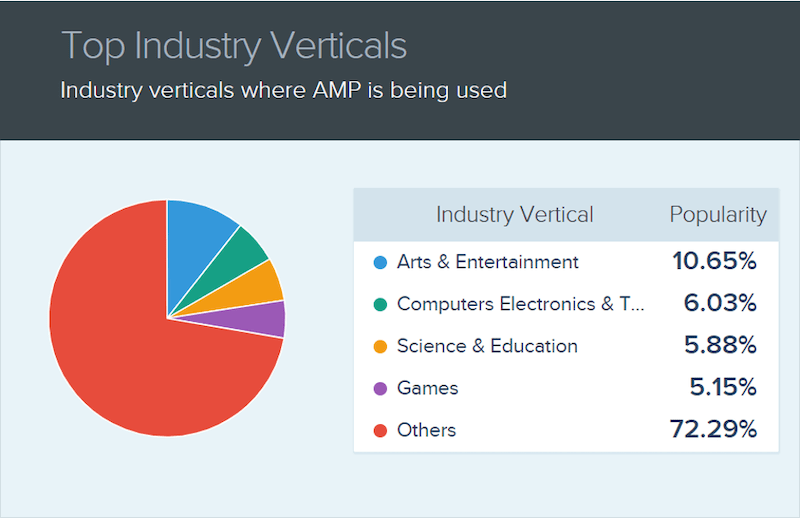
While many popular websites are using AMP technology today, such as Yahoo, CNN, BBC, Reddit, Washington Post, WordPress, Gizmodo, Wired, Independent.co.uk, Pinterest, eBay, and many more—it is not a technology reserved only for big brands. AMP technology is being used by over 1.4 million websites. The chart below shows which industries are using AMP the most:
- Arts & Entertainment accounts for nearly 11% of total AMP technology usage.
- Computer Electronics & Technology accounts for about 6%.
- Science & Education is close behind at 5.88%.
- Gaming accounts for about 5.15% of AMP technology usage.
- The remaining 73% is the total of every other industry’s insignificant percentages
The anatomy of a Google AMP page
To understand how Google AMP gives your SEO and content marketing strategy a boost, it’s best to first get a grasp on the three core components of an AMP page.
AMP HTML
AMP HTML differs from regular HTML (or HTML5) in that it comes with mobile-focused properties and custom tags. AMP HTML guarantees certain baseline performance characteristics—which translates to content loading faster on users’ devices. This means faster consumption by the reader and a better overall user experience, which can impact conversion rates and SEO/content marketing metrics like bounce rate (mentioned above) and time on site. (Faster consumption means the reader can consume more articles in less time).
Speaking of user experience, are you up to speed on Google’s upcoming page experience update?
AMP JavaScript
AMP JavaScript enables the AMP page to more efficiently provide the core benefit of the regular page to the reader. The AMP JavaScript library employs AMP’s top practices like inline CSS and font triggering—which ensure faster rendering of the AMP page for readers. It also allows for performance enhancement techniques, like pre-calculating the layout of every page element before resources are loaded, and disabling slow CSS selectors—all of which are crucial to the reader’s experience.

AMP Cache
The AMP cache is built to serve only valid pages and to let them pre-load safely and efficiently. What this means is, a confirmed page (which we’ll get to later) is guaranteed to work, eliminating dependency on external factors that could slow the page down.
Given the below breakdown, you can see that by cutting back on the HTML code tag management and loading only the page elements that are suitable for mobile users, the AMP version of a page renders more quickly. Will Critchlow’s Whiteboard Friday diagram provides a simple visual for this:
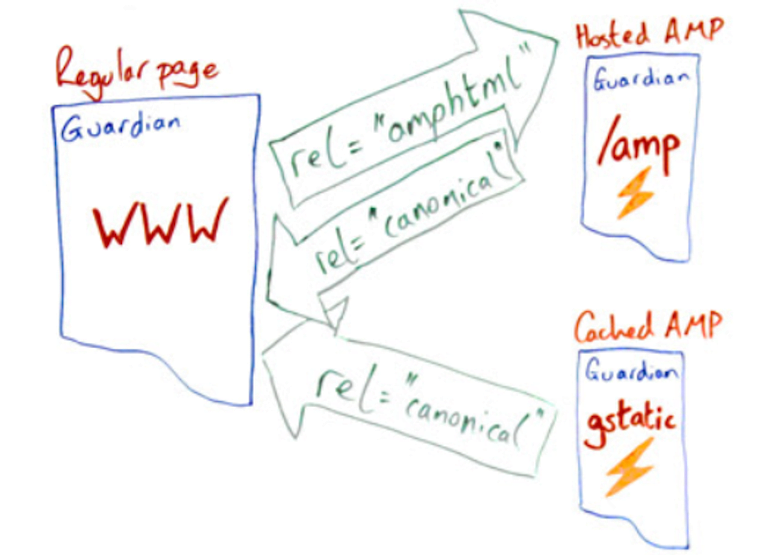
As Critchlow notes, if you have an AMP version, in the source code, you would designate that with the rel AMP HTML link. For example, if you put /amp at the end of any news story on The Guardian website (even on desktop), you’ll see the AMP HTML. It’s linked in display with the AMP HTML link in the source code. You can also see the AMP difference:
Here’s a regular Guardian news story page:
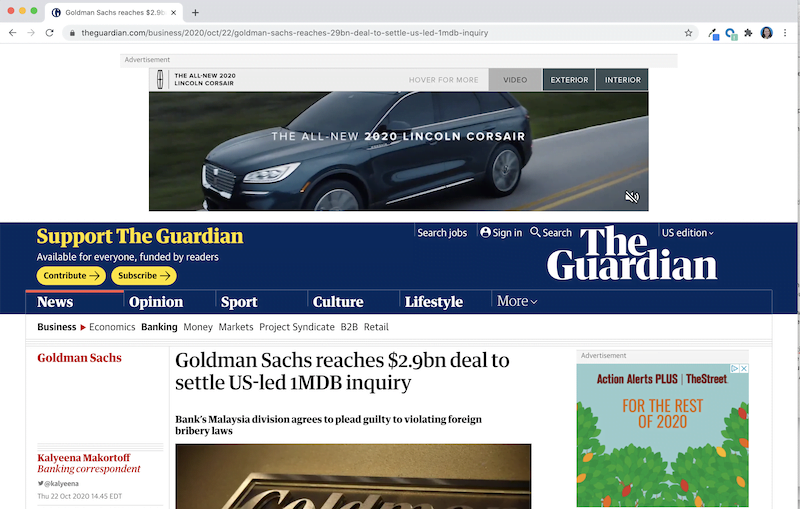
And here’s the AMP version of that same Guardian news story page:
That is, after adding “/amp” at the end of the link.
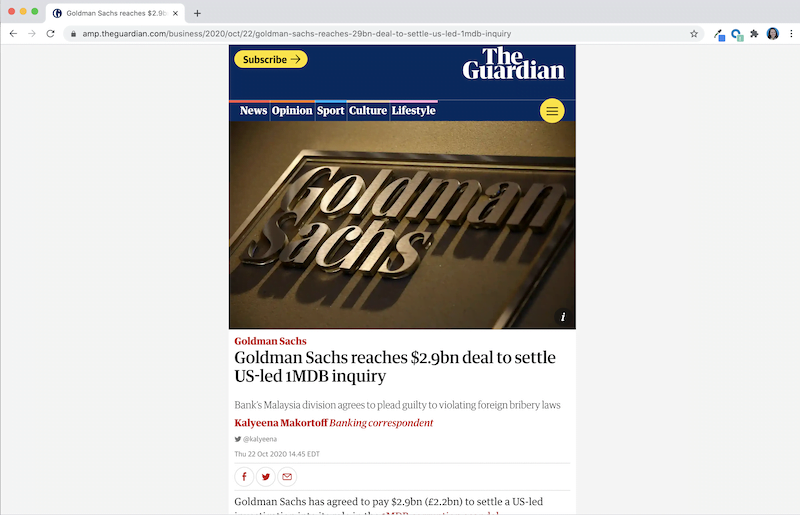
Without the ads, menu navigation, recommended reads, and other resource-heavy elements, the page loads faster and is a simpler experience for the reader.
Drawbacks and additional considerations for integrating Google AMP
While AMP can help to improve your ranking as well as the experience and performance of your content to mobile readers, it does have drawbacks and caveats which you should consider when deciding whether to implement AMP for your site:
- To begin with, adopting AMP pages entails sacrificing a significant number of UX elements on your webpage. At its core, AMP HTML prioritizes efficiency over creativity, so if engaging visuals is a big part of your web experience, this may not be for you.
- In addition to limited images on your AMP pages, you’ll also only be allowed one advertisement per page. This limiting framework also doesn’t support disruptive ads like expendables, while direct-sold ads can be difficult to implement.
- From a marketing perspective, it costs double the crawl for one piece of content, part of Google’s thrust to ensure parity. For many publishers, it’s been found to drive impressions but not necessarily engagement metrics. This is due to the Top Stories carousel that encourages users to read from other sources.
- In a similar vein, Google’s AMP viewer tends to dilute brand identity as a Google domain is shown in the address bar. While there is a fix to show the actual site on top of the AMP page, it takes up precious space above the fold. You may also not achieve the same brand feel with a Google AMP page vs a standard page, as seen with the example below:

- As well, AMP only works if users click on the AMP version of a webpage (instead of the canonical version). And while studies have found that the AMP library can reduce the number of server requests to fetch a document by as much 77%, the AMP version is not always served if it’s not implemented correctly.
- While AMP has been around for four years, it’s still relatively in its nascent stages.
Here are some final details about Google AMP that must be considered when deciding whether to implement it on your site.
- You need to use a streamlined version of CSS.
- You’re only allowed to use the JavaScript library that AMP provides, and because you’re not in control, you could experience lazy loading (perhaps the only downside of AMP).
- AMP sites must be properly validated if they are to work every time.
- AMP plugin pages don’t allow forms.
- Custom fonts need to be specially loaded for better experience.
- You need to declare image heights and widths.
- You need AMP-approved extensions if you want video content on your pages.
Finally, AMP prioritizes speed and readability, not shareability. So because your social sharing buttons are created using JavaScript, they may not display properly.
AMP prioritizes speed and readability, not shareability.
How to implement AMP to improve your content and SEO
Of course, if you have a WordPress site, the simplest way to start implementing AMP is to use the official AMP plugin from WordPress and Google. If you’re looking to have more control over how your AMP pages look or gather analytics more easily, you might try other free plugins such as WeeblrAMP or AMP for WP.

However, not all businesses use WordPress, and plugins do have their limitations. So I’m going to walk you through the steps you can take to implement AMP technology into your content marketing strategy without a plugin.
Step #1: Create your AMP page template
The first step you’ll need to take to implement AMP for your blog posts and other high-quality content is to create an AMP page template from scratch. To create an AMP page template, you’ll need to start your AMP HTML page with <!doctype html> at the top of your page, and identify the page as AMP content by adding a lightning bolt symbol (?) in the HTML tag like this <html ?>.
Here’s an example of a simple AMP HTML page which you can use for your content:
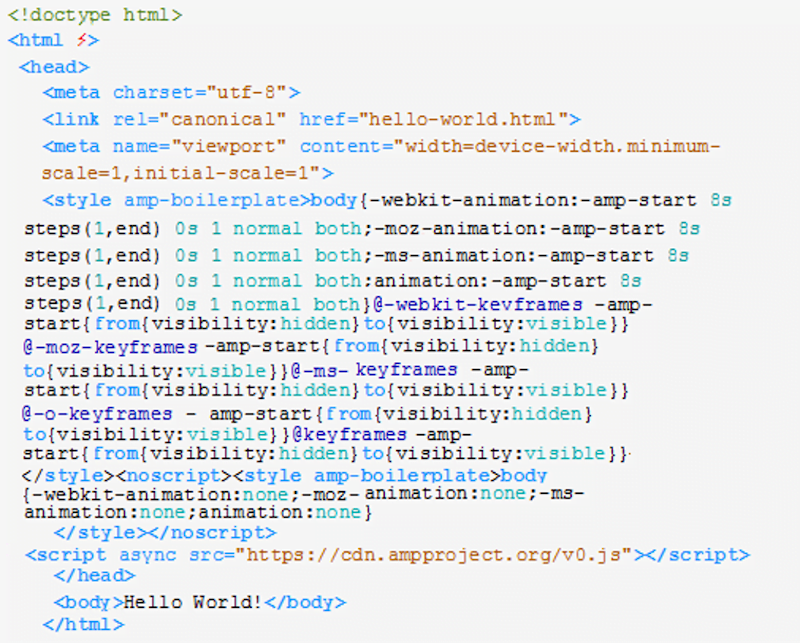
These are the tags to include in your AMP HTML documents:
- <head> and <body> tags
- <meta charset=”utf-8”> as the first child of your <head> tag
- <script async src=”https://cdn.ampproject.org/v0.js”></script> inside your <head> tag to include and load the AMP JavaScript library
- <link rel=”canonical” href=”$SOME_URL”> inside your <head> tag
- <meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width,minimum-scale=1,initial-scale=1”> inside your <head> tag
- AMP boilerplate code in your <head> tag
These tags are those which you can change in the code of the pages themselves:
- link href=”hello-world.html”
- The content within the body section <body>Hello World!</body>
Now that you know how to create an AMP page template for your blog, you might want to learn about all of the HTML tags you can use for your AMP pages.
Unfortunately, there are some HTML tags that you can’t use for AMP pages. These include:
- <frame>
- <frameset>
- <object>
- <param>
- <applet>
- <embed>
- <base>
- <input elements>
Step #2: Preview and validate your AMP page
To preview your AMP page, you’ll need to open your page directly in your web browser from your file system, or use a local web server, such as Apache 2.
To make sure your AMP page is valid, on the other hand, all you have to do is open your page in your web browser, add “#development=1” to the URL, and then open the Chrome DevTools console to check for validation errors.

Bruce Day recommends testing one to two types of pages from your website on AMP first. Ideally, you should also include some pages that rank so you can see if Google is serving the AMP version in mobile search results.
It’s important to note that it could take a couple of days for Google to find, check, and index the AMP version of a page. As well, you should let the rollout run for at least a month (longer if you can afford to do so). This allows you to build enough data to ensure that rolling out AMP sitewide is worth it.
It can take a couple of days for Google to find, check, and index the AMP version of a page, and you should run your AMP pages for at least a month in order to gain meaningful data.
Step #3: Track performance
As with anything in digital marketing, you need to track the performance of your AMP pages. Not just to see how you compare with your competitors, but also to see if your performance is aligned with your goals.
You can use in-house tools to do this, such as Google Analytics, or any of the various third-party B2B tools. There are a number of analytics vendors that provide built-in features for AMP analytics.
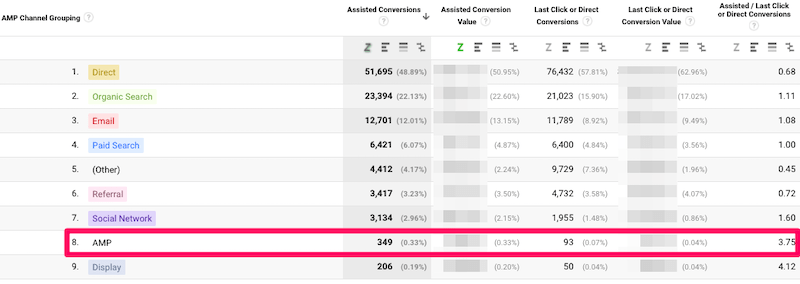
Other important things to note include using canonical URLs and other variables to define what should be recorded. This is crucial for identifying any traffic fluctuations caused by AMP.
Additionally, the extraUrlParams attribute in amp-analytics adds a query string parameter to the canonical URL (such as “type=amp”). This makes it easier to differentiate AMP pages from normal web pages in analytics. This enables you to compare total traffic on pages before and after AMP launch.
Canonical URLs enable you to isolate AMP traffic in Google analytics for better tracking and optimizaiton.
Is AMP right for you?
As you’ve learned, AMP is a great way to speed up web pages, ultimately, providing better UX in your content delivery, particularly for mobile users. If, based on your business model and the criteria above, it is deemed right for your business, be sure to take the above considerations into account and to follow the steps for implementation. It may take some time, but having better-performing content affords long-term benefits.
About the author
Aaron Chichioco is the chief content officer (CCO) and one of the web designers of Design Doxa. Aside from his expertise on web/mobile design and development, he also has years of experience in digital marketing, branding, customer service, ecommerce and business management.







